Butt Welding Machine
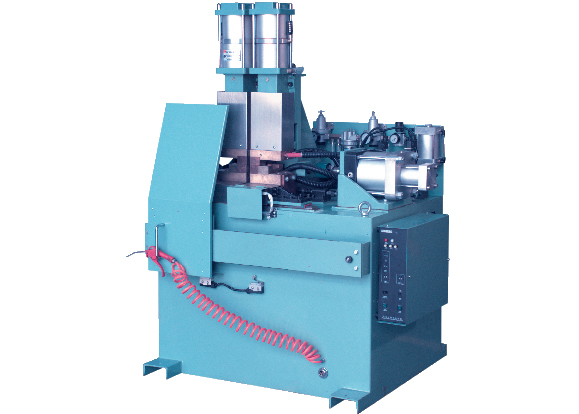

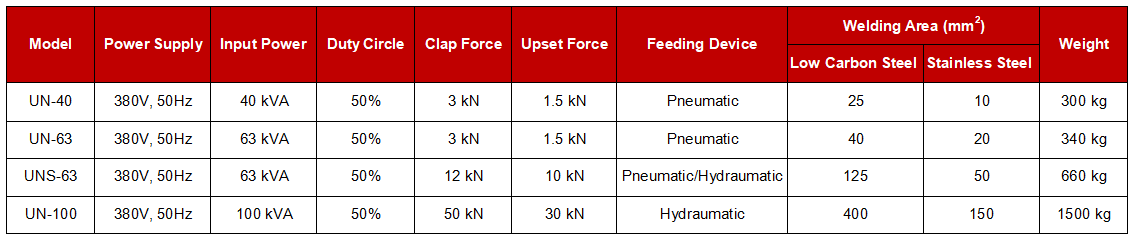
- Power Supply: 380V 50Hz
- Input Power: 40~100 kVA
- Duty Circle: 50%
- Clap Force: 3~50 kN
- Upset Force: 1.5~30 kN
- Feeding Mechanism: Pneumatic, Hydraumatic
- Welding Area: 25~400 sq.mm (Low Carbon Steel)
- Welding Area: 10~150 sq.mm (Stainless Steel)
Technical Specification of Butt Welding Machine
Butt Welding Machine Structure and Working Principle
Butt Welder Structure
The butt welding machine is mainly composed of welding transformer, left electrode, right electrode, AC contactor, feeding mechanism and control components.
The feeding mechanism is to realize the melting and extrusion process required in the welding process. It mainly includes the groove in the groove, the sliding plate and the adjusting screw. When the joystick moves in the two-stage limit position, the maximum working stroke of the electrode can be obtained.
The control program of the control element is: press the contactor button, turn on the relay, make the AC contactor work, and then the welding transformer is turned on. Move the joystick to compress the two weldments and energize to heat.
Butt Welding Machine Working Principle
The electrodes of the butt welding machine are respectively installed on a fixed plate and a sliding plate. The sliding plate can move along the guide rail on the fuselage. The current is transmitted to the electrode through the secondary coil of the transformer. When the pressure mechanism is pushed, the ends of the two steel bars come into contact with each other. After that, the short-circuit resistance generates heat, which heats the ends of the steel bars. When they are heated to high plasticity, they are squeezed with force to achieve a firm butt joint between the ends.
Flash Butt Welding Machine
Butt welding machines are divided into different welding methods: flash butt welding machine, steel bar butt welding machine, copper rod butt welding machine
Flash butt welding mainly uses the heat generated by the contact resistance of the workpiece to heat the workpiece, the metal surface is melted, the temperature gradient is large, and the heat-affected zone is relatively small.
The weld is to form a common crystal grain under the condition of plastic deformation of the counterpart solid metal of the workpiece. The structure and composition of the weld are close to the basic metal (or after heat treatment), and it is relatively easy to obtain a welded joint of equal strength and plastic.
The flashing process has the self-protection function of exhausting air and reducing metal oxidation. Upsetting can also discharge oxides with the liquid metal out of the weld. There are fewer defects such as weld inclusions and incomplete penetration.
The flashing process has a strong self-adjustment function, and has low requirements for strict compliance with specifications, and the welding quality is stable. The unit welding cross-sectional area requires low electric power, and only (0.1-0.3) KVA/mm2 electric power is required for welding mild steel.
Welding productivity is high, and it only takes a few seconds to tens of seconds to weld a joint.
Features of Butt Welding Machine
The standard configuration controller can be used to analyze and adjust the parameters of the welding process, such as clamping, welding, upsetting, maintenance, and rest. The equipment is easy to operate and easy to master.
The resistance butt welding process is simple, the amount of weldment shortening is small, and there is little burr, which is beneficial to simplify the subsequent process.
Suitable for wire butt welding of low carbon steel, pure copper, brass, stainless steel and other metals.
The use of a new generation of controller can realize the optimal control of flashing and upsetting during the entire welding process. It is reliable and high in accuracy. Compared with ordinary resistance butt welding machines, the power supply capacity required for welding workpieces of the same cross section is small. Low energy consumption.
The hydraulic system of the welder is equipped with a precise regulating valve, which can realize the stepless adjustment of the flashing speed, ensuring the stability of the flashing process, and reducing the slag inclusion of the welding workpiece joint, with good metallography, strong and beautiful appearance.
It is widely used for butt welding between carbon steel, alloy steel, non-ferrous metal pipes, rods, plates, and profiles or for butt welding between dissimilar metals.
Send Message
Catalogue
News & Technicals
Analyze the Electrode of the Intermediate Frequency Spot Welder
Analyze the Influence of the Welding Point Distance of the Spot Welder
Function of Butt Welding Machine Inspection System
Contact Us
Email: info@resistancewelder.com
Tel: 0086-185-6889-5678
Factory: No.81 Donghui Second Street, Huangpu District, Guangzhou
